Table of Contents
Get to know WLAN Controller
Components of WLAN
There are several components of a WLAN, including:
Mobile or Desktop PC
Access Point
WLAN Interface
The WLAN interface acts as an access point (AP) that the client can use to connect to the node. The interface can provide connectivity from the AP to the WLAN gateway (GW) server for WLAN users and access, and for WLAN mobility management.
Antena
The antenna on the WLAN is for transmitting signals. Of course it is very important to include; wider area. With a good and correct antenna position, the WLAN can cover many devices by transmitting signals.
LWAPP is
LWAPP stands for Lightweight Access Point Protocol. This LWAPP is used to define the AP authentication process with the controller, distribute firmware and configuration, and define transport headers for LWAPP traffic.
LWAPP mechanism in network
- LAP sends DHCP discover packet to get IP Address from DHCP Server, unless LAP has been set to use Static IP.
- LAP then sends LWAPP discovery request messages to WLC.
- WLCs that receive LWAPP discovery request messages respond with LWAPP discovery response messages.
- From the LWAPP discovery response received by LAP, LAP selects WLC for registration.
- LAP then sends an LWAPP join request to WLC and waits for an LWAPP join response.
- WLC validates LAP and sends LWAPP join response to LAP.
- LAP validates WLC, which completes the discovery and join process. The LWAPP join process includes mutual authentication and encryption key derivation, which will be used for security in the join process and future LWAPP control messages.
- LAP sends DHCP request to DHCP Server to get IP Address, unless LAP has been set to use Static IP.
- If layer 2 LWAPP mode is supported by LAP, LAP will broadcast LWAPP discovery messages in layer 2 LWAPP frames. WLC connected to the network and configured with layer 2 LWAPP mode will respond with a layer 2 discovery response. If the LAP does not support layer 2 mode, or if WLC or LAP fails to receive an LWAPP recovered response to the layer 2 LWAPP discovery message broadcast, the LAP will proceed to step 3.
- In step when, LAP will start layer 3 LWAPP WLC Discovery.
- If step 3 fails, return to step 1.
How WLAN Controller Works
Features
- Interference detection and avoidance; the RF power and channel assigned will be matched as planned.
- Load Balancing; control is disabled by default. High-speed load balancing can be applied to link users to multiple access point gateways for greater coverage and data rates.
- Coverage Hole Detection and Correction; part of RF control that handles power levels (power levels). Power can be increased to cover the “holes” or decreased to protect against overlapping cells.
- The WLAN controller is also equipped with various authentication models, such as 802.1X (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP), LEAP, EAP-TLS, WiFi Protected Access (WPA), 802.11i (WPA2), and Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP).
Background of the emergence of WLAN Controller
What Happens When There Is No WLAN Controller
What are the advantages of using a WLAN Controller
- Using the Wireless Controller allows you to provide centralized management of the wireless network.
- With the help of Wireless Controller we can configure all access points at once.
- Single Network exit/entry point for client traffic providing security.
- Access points that are not connected to the Wireless Controller cannot provide services to clients.
- The Wireless Controller can authenticate the AP to prevent the rouge access point from being on the network.
- Client devices can roam seamlessly in the wireless network.
- The Wireless Controller acts as an authenticator, so you must configure one device instead of 100 to handle authentication.
- Wireless Controller allows access points to share RF information.
- Can easily add access point to Wireless network. And after connecting to the wireless controller, it can start working.
About Aruba Controller
Aruba Controller Wireless Network
- Controller-based, where all access point management is centralized in one wireless controller, so that all existing wireless networks can be integrated and easy to carry out monitoring.
- Controllerless (Instant Access Point) where the Access Point can be a semi controller to manage some APs and clustering in a small scope.
- Aruba Central, designed to simplify deployment, management and optimization of Wireless, LAN, VPN and SD-WAN on a large scale focused on the Aruba Cloud environment.
Aruba Controller Wired Network
Aruba provides many switch options for various purposes from Managed Switches and Unmanaged Switches, to layer 2 to layer switch needs. Then when you buy an Aruba switch, you don’t need to buy an additional license for each switch you buy.
Clearpass
How to Set Aruba Controller
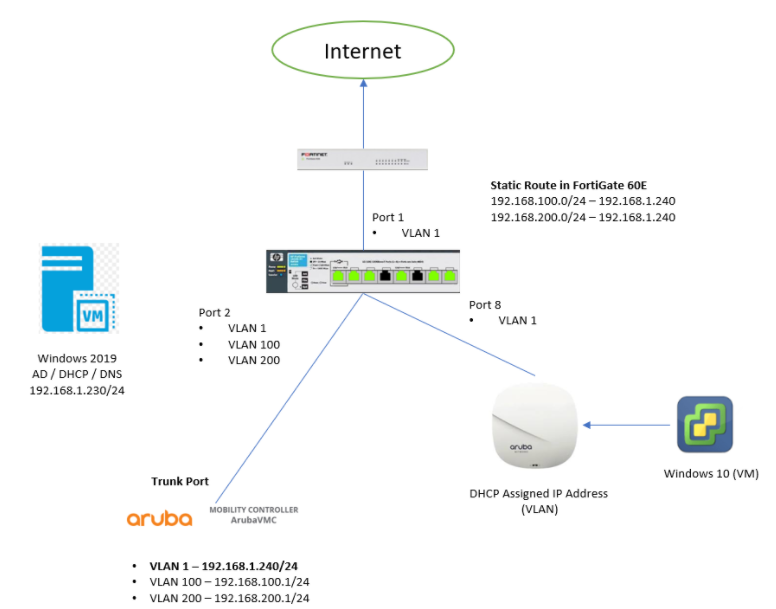
2 Static Routes created in FortiGate to route 192.168.200.0/24 to Aruba VMC (192.168.1.240)
Aruba Controller Preparation
- Download Aruba Virtual Mobility Controller – ArubaOS_VMC_8.6.0.3_74788.ova
- Convert OVA to OFV and import to ESXi 6.7 Host with PowerCLI
- 3x CPU, 4GB RAM, 4GB and 6GB HDD and 2 x vNIC required for Aruba VMC
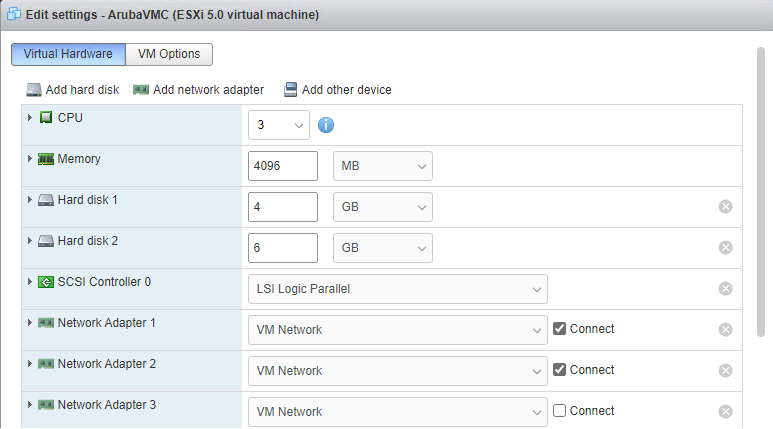
Aruba Controller Initial Settings
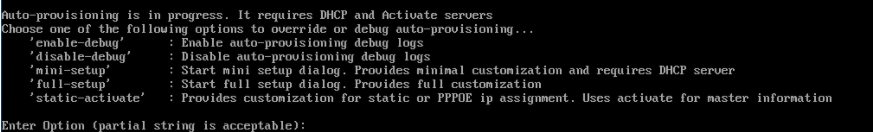
- Turn on Aruba VMC and select Full Setup
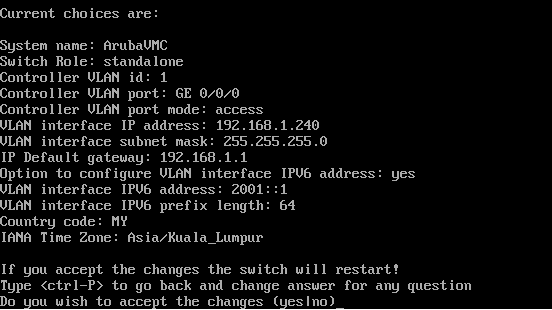
- Select Switch Role = Standalone and other information, such as System Name, IP Address, Country Code, and Time Zone when prompted. Click Yes to accept the changes to complete the initial configuration.
- Login to with the credentials specified during initial setup.
License Evaluation
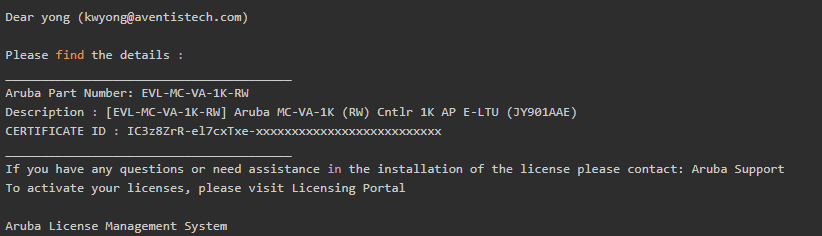
- Request an Evaluation license from a local Aruba Distributor, and you will receive an Email with a Certificate ID as below:
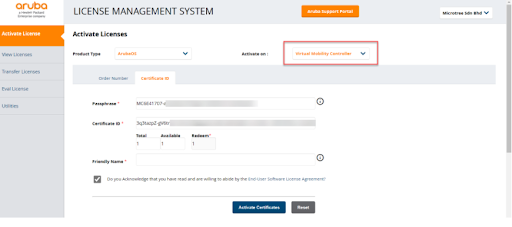
- Login to Aruba License Management System activate license with Certificate ID & Passphase

- Select Virtual Mobility Controller, and enter **Passphrase and Certificate ID
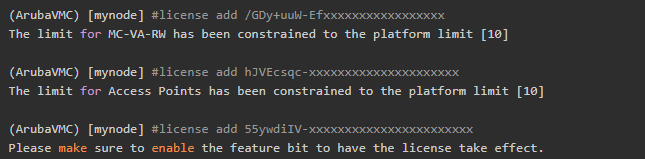
Add license to Aruba Controller Aruba VMC using CLI:
- The MC-VA-XX license is a shareable license required to stop the AP on the virtual controller
- An AP license is required for every operational, mesh, or remote LAN-connected AP that advertises at least one BSSID (virtual AP).
- One operational AP that uses one or more Policy Enforcement Firewall (PEF) features, such as intelligent application identification, policy-based traffic management and control, or a steateful user firewall.
Convert Aruba Controller 315 To Campus AP
- Convert Aruba IAP to Campus AP with controller IP Address
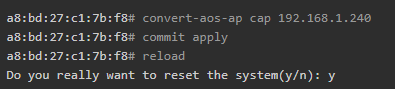
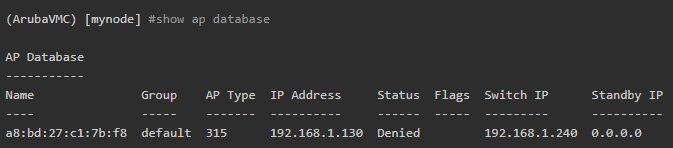
- Verify that the Access Point is registered in the Aruba VMC database now
- Create an AP Group named LAB

- Whitelist the AP’s mac address and approve it by associating it to the AP Group

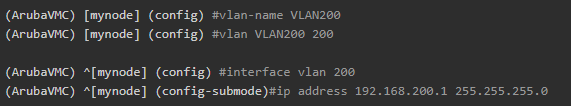
VLAN, IP Interface And DHCP Pool
- Create a new VLAN 200 and IP Interface
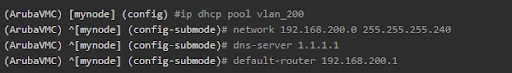
- Create DHCP Pool for VLAN 200 with smaller subnet
- You will get below error message if you try to create DHCP Pool with more than 256 hosts (/24)

DHCP Relay
Don’t create DHCP Pool in Aruba VMC, and configure DHCP Helper on VLAN interface as below:
- Configure Aruba VMC port as trunk port

- Configure Helper IP Address on Interface VLAN 200

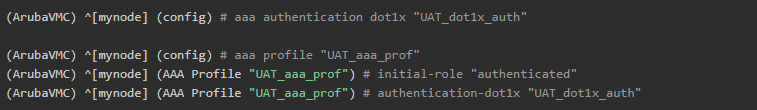
AAA Authentication Profile
Create a new AAA Authentication profile
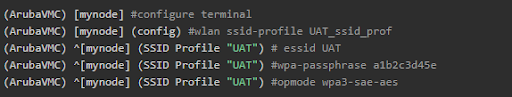
SSID Profile With WPE3 Authentication
Buat Profil SSID baru dengan WPE3. Sebagai catatan, WPE3 hanya support untuk tunnel mode.
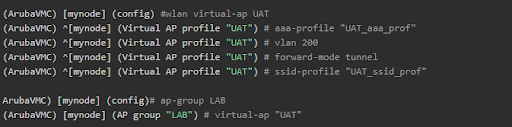
Virtual AP
Create a new Virtual AP and add it to the AP group
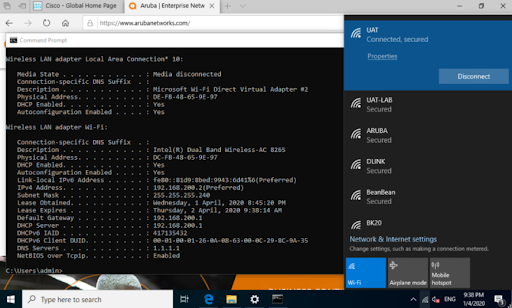
Testing Aruba Controller on Windows 10
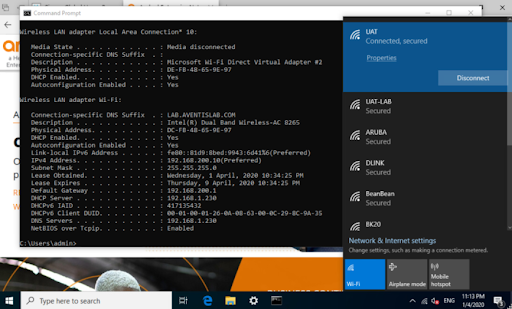
Get IP Address from Aruba VMC
Conclusion
That’s the information about the Aruba Controller and how to set it up. For more information, you can visit the NETDATA web page. NETDATA also officially sells various products from Aruba at affordable prices because it is an official partner of Aruba.
![]()


